- ホーム
- 総合研究所
- 総合研究所 概要
- 事業年報
- 平成28年度 事業年報
- 亜熱帯性植物に関する事業について
- 6)Kalanchoe Project

亜熱帯性植物の調査研究
6)Kalanchoe Project
Ratchada Sangthong - Plant Laboratory*1
Plant tissue culture and induced mutation procedures can contribute to crop improvement with cost and time effective. The purpose of this project is to establish genetic variability of plant germplasms and novel varieties of Kalanchoe for obtaining the new phenotypes such as changes in plant height, plant architecture, flower shape, pigmentation, number of leaves and branches, yield potential and size as well as utilizing against environmental stresses.
Kalanchoe Churara varieties were used as plant materials for petal culture and induced mutagenesis using chemical mutagen and ultraviolet light. Basal plant growth medium for in vitro culture was Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium containing 3% sucrose and 0.8% agar, pH 5.8.
1) Petal culture
For petal culture, bloom flowers of Kalanchoe were collected from greenhouse plants and the petals were cut for surface sterile before performing the experiment. Aseptic petals were placed onto 50 formulae of MS medium supplemented with various combinations of plant growth regulators (PGR).
Organogenesis was occurred from petal pieces (Fig. 1B, 1C) after culture on suitable medium formula for 1-2 months. Regenerated shoots (Fig. 1D) were then transferred onto MS basal medium for growing into the complete plants (Fig. 1E).
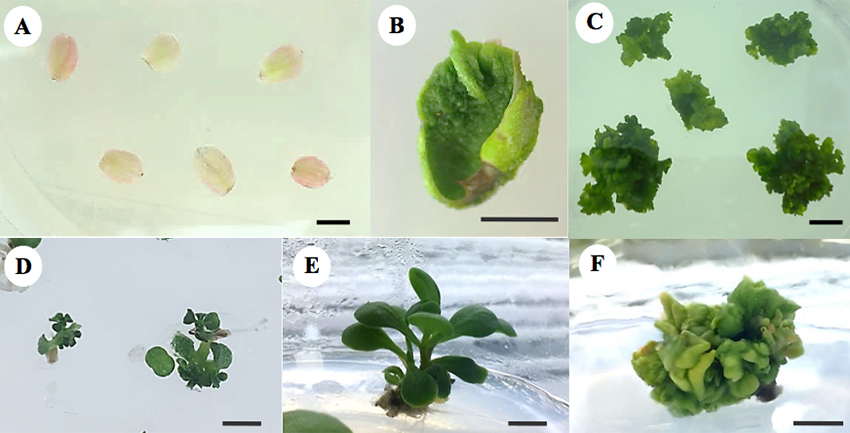
Figure 1 Petal culture of Kalanchoe (bar = 1 cm) after culture on suitable medium for (A) 1 Day and (B) 1 month. (C) Organogenesis after 2 month. (D) Regenerated shoots after 3 months. (E) Complete plant after 4 months. (F) Abnormal shoots from unsuitable medium formula after 4 months.
2) Induced mutagenesis using chemical mutagen
Chemical treatments using sodium azide (SA) was applied to in vitro shoots of Kalanchoe. Optimum dosage range of SA could cause some morphological changing of leaf and shoot such as large leaf (Fig. 2B), succulent shoot (Fig. 2C) and elongate shoot (Fig. 2D) observed at 1-3 month after treatment.
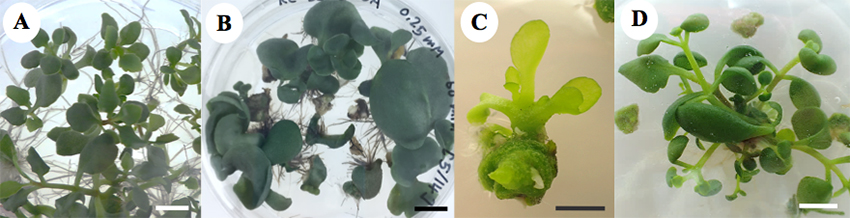
Figure 2 Characteristics of in vitro shoots of Kalanchoe treated with sodium azide after 1 month (bar = 1 cm). (A) In vitro shoots (control). (B) Expanded leaves. (C) A succulent shoot. (D) Elongate shoots.
3) Induced mutagenesis using ultraviolet light
In vitro shoots of Kalanchoe were cultured under ultraviolet light (UV-C, 254 nm). Morphology changes of treated cultures were found comparing with control shoot cultured under fluorescent light such as succulent shoots with small leaves (Fig. 3B) and elongate shoots (Fig. 3C).
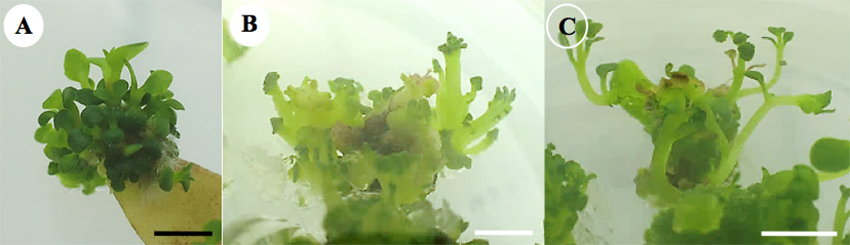
Figure 3 Effect of UV light treatment in Kalanchoe at 2 months (bar = 1 cm). (A) In vitro shoots (control). (B) Succulent shoots with small leaves. (C) Elongate shoots.
With plant tissue culture technology, petal culture and induced mutation systems of Kalanchoe were established in plant laboratory and provided the possibility to create the new sources of plant germplasms. The potential lines for supporting the flower business with new characteristics will further be screened and selected in greenhouse.
*1植物研究室
Copyright (c) 2015 Okinawa Churashima Foundation. All right reserved.